Introduction
For the past decade, our colleagues and columnists have remorsefully muttered about friends in terminally ill colleges. Now, we know “for whom the bell tolls.” As more old colleges are thrown on the death cart, other small colleges only wait and wonder if their college is next to be chucked on the heap of history.
This paper introduces a Vulnerability Gauge to predict if a private college or university is or is not at risk of financial failure. A logit regression tested the model with several different combinations of variables. The model was applied to a random sample of forty-four private colleges and universities drawn from the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System[1] (IPEDS). database. The tests found the most robust and parsimonious model had an 86.3% prediction rate of financial risk when these two factors were used:
- Annual percentage change in unrestricted net assets over five-years (for most private colleges, these assets represent the ready financial reserves that cover operational expenses);
- The total change in FTE (full-time enrollment) over five-years.
The logit regression yielded the probability of financial failure for each school in the sample. The probabilities were then arrayed into four risk bands: low, moderate, greater, and high risk of financial failure as shown in Table 1. The risk bands indicate that the lower the probability, the lower the risk of closing and the higher the probability, the greater the risk of closing.
Table 1
Risk Bands of Probabilities for Study Sample

Findings from Large Sample Analysis of Unrestricted Net Assets and Enrollment
After the random sample was tested, the model was then employed to test the vulnerability of 949 private colleges that were open in 2016. This sample excluded medical schools, research institutes, arts programs, seminaries, and other specialty colleges. The analysis covered the period 2016-17 to 2021-22, which was the most recent year in which IPEDS higher education data was available.
Chart 2
Colleges Assigned to Two Classes of Risk and Enrollment for 2021 and 2022
Here are several observations from Charts 2:
- In 2021, 255 private colleges with less than or equal to 2,000 students were rated at greater to high risk, but only 37 colleges with more than 2,000 students were rated with the same risk. In other words, institutional size seems to be a major factor in determining risk. In 2021, the risk rating for small colleges was 6.9 times greater than for larger colleges.
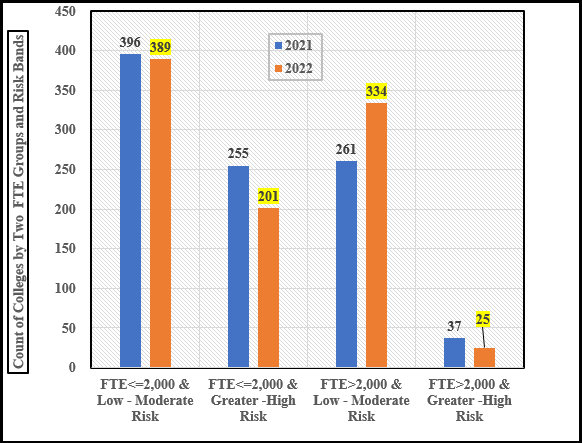
- In 2022, 201 more smaller colleges than larger rated as greater to high risk, 54 fewer colleges than in 2021. Yet, the greater to high-risk rating for smaller colleges was 8.0 times larger than larger colleges.
- In 2022, the enrollment group with more than 2,000 students saw seventy-three more colleges rated as low to moderate risk, in comparison to 2021, but this group had twelve fewer colleges rated as higher to greater risk.
Conditions Unique to Higher Education that Degrade Response to Risk
Before any remedy can be prescribed, we need to understand why so many private colleges are slow to respond to economic and financial threats to their existence. The list at the start of this paper identified several factors that shape financial stress, but there are further internal and operational issues that also shape the financial vulnerability at small private colleges.[2] See the following list of issues that may foster financial stress.
- Contradictions of dual governance, where major academic financial problems, and their solutions may be stymied by conflict between how faculty and administration govern their respective areas.
- Faculty tenure that places costs, sometimes substantial, for the dismissal of faculty due to a major reorganization and the termination of academic majors or programs.
- Explicit and implied contracts with students, faculty, and external parties in student handbooks that set out the liability to students when programs, athletic programs, student services, or dormitories are ended or downsized, faculty handbooks that specify work conditions, alumni traditions that carry costs, or unstated relationships with local governments that have inherent costs.
- Accreditation and governmental regulations that may stipulate financial conditions to sustain operations and standards for academic programs and student services that can a) raise the cost of operations and b) make it difficult to change academic programs. Governmental regulations can also stipulate financial conditions and standards for maintaining eligibility for federal funds or for compliance with federal mandates.
- State Non-Compete Regulations can keep a college from offering a new program if another institution already offers it.
- Human Capital, buildings and equipment may not match what a college needs during a strategic reorganization to serve its student market better while reducing costs.
Besides the preceding organizational failures, leadership failures by the president and board of trustees to reshape a private college’s capacity to rapidly respond to financial crisis and reducing financial vulnerability
Potential Remedies for Reducing Financial Risk
Responding to the highest level of financial risk requires information that delineates the financial, operational, and market conditions of the institution. Before diving into strategic and operational turnaround strategy, the president and board need to acknowledge whether or not operational deficits have become a recurring and increasing threat. In the next step, both the board and president need to know the level of financial reserves currently available, whether those reserves are expanding or shrinking, and how long those reserves will last, if there are operational deficits. Also, there is no surer sign of performance inefficiency than a major with three or more full-time faculty instructing four students in a major.
It is imperative for Boards to recognize the need to support Presidents who lead with fortitude, intelligence, and foresight, otherwise it will be difficult for the institution to withstand conflict generated by internal and external dissension in response to major strategic changes. Conflicting solutions and dissension could become a regular event. Nonetheless, every day lost, before taking steps to overcome the inertia toward failure, will push the college closer to its demise.
The factors that make up the Vulnerability Gauge can guide the development of an effective strategy to generate larger and positive net incomes that increase unrestricted net assets. Focusing on factors in the Vulnerability Gauge will lead to optimizing markets, generating higher cash flows from tuition, cutting administrative expenses, improving the financial and operational relationship between faculty and students, imposing controls on the operational efficiency of capital investments in grounds, buildings, and equipment, and moving revenue generating centers toward positive contributions to the bottom line.
For colleges that have arrived at the brink of survival, there seem to be three strategic options that colleges at the brink of extinction consider:
- Merger
- Forming a partnership;
- Looking for wealthy alumni or local donors.
To access the Vulnerability Gauge, Go To: Education Consulting & Strategic Planning for Colleges & Schools – Stevens Strategy